队列
队列是一种受限的线性表,它允许在一段进行删除操作,在另一端进行插入操作。
可以用数组实现,也可以用链表实现。
数组实现(顺序存储)
设立一个队头指针front,一个队尾指针rear,分别指向队头元素和队尾元素,rear-front为元素个数。
(数组实现中,其实就是下标。)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
| #define MAX_SIZE 10
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Queue
{
DataType queue[MAX_SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
}SeqQueue;
void initQueue(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return;
}
SQ->front = SQ->rear = 0;
}
bool isFull(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return false;
}
if (SQ->rear == MAX_SIZE)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool isEmpty(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return false;
}
if (SQ->rear == SQ->front)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool pushQueue(SeqQueue* SQ,DataType data)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return false;
}
if (isFull(SQ))
{
return false;
}
SQ->queue[SQ->rear] = data;
SQ->rear++;
return true;
}
void printQueue(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (isEmpty(SQ))
{
return;
}
int i = SQ->front;
while (i < SQ->rear)
{
cout << SQ->queue[i]<<" ";
i++;
}
cout << endl;
}
bool popQueue(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ || isEmpty(SQ))
{
return false;
}
for (int i = SQ->front; i < SQ->rear; i++)
{
SQ->queue[i] = SQ->queue[i+1];
}
SQ->rear--;
return false;
}
DataType getFront(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return -1;
}
return SQ->queue[SQ->front];
}
bool destoryQueue(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return false;
}
SQ->front = SQ->rear = 0;
return true;
}
int getElemsNum(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return 0;
}
return SQ->rear-SQ->front;
}
|
链表实现(链式存储)
为了操作上的方便,我们将队头指针指向链队列的头结点,而队尾指针指向终端结点。
就是简化了单链表,加了些条件限制(一边进,一边出。)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
| typedef int DataType;
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct Qnode
{
DataType data;
struct Qnode* next;
}Qnode;
typedef Qnode* QueuePtr;
typedef struct Queue
{
int length;
QueuePtr front;
QueuePtr rear;
}LinkQueue;
bool initLinkQueue(LinkQueue* LQ)
{
if (!LQ)
{
cout << "S";
return false;
}
LQ->length = 0;
LQ->front = LQ->rear = NULL;
return true;
}
bool isEmpty(LinkQueue* LQ)
{
if (!LQ)
{
return false;
}
if (!LQ->front)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool isFull(LinkQueue* LQ)
{
if (!LQ)
{
return false;
}
if (LQ->length == MAX_SIZE)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool pushQueue(LinkQueue* LQ, DataType num)
{
if (!LQ)
{
return false;
}
Qnode* node = new Qnode;
node->data = num;
node->next = NULL;
if (isEmpty(LQ))
{
LQ->front = LQ->rear = node;
}
else
{
LQ->rear->next = node;
LQ->rear = node;
}
LQ->length++;
return true;
}
bool popQueue(LinkQueue* LQ)
{
if (!LQ || isEmpty(LQ))
{
return false;
}
Qnode* tempnode = LQ->front;
LQ->front = LQ->front->next;
delete tempnode;
LQ->length--;
if (!LQ->front)
{
LQ->rear = NULL;
}
return true;
}
void printQueue(LinkQueue* LQ)
{
if (!LQ || isEmpty(LQ))
{
return;
}
Qnode* tempnode = NULL;
tempnode = LQ->front;
while (tempnode)
{
cout << tempnode->data<<" ";
tempnode = tempnode->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
bool clearQueue(LinkQueue* LQ)
{
if (!LQ)
{
return false;
}
Qnode* tempnode = NULL;
while (LQ->front)
{
tempnode = LQ->front->next;
delete LQ->front;
LQ->front = tempnode;
}
LQ->front = LQ->rear = NULL;
LQ->length = 0;
return true;
}
bool getFront(LinkQueue* LQ, DataType* recv)
{
if (!LQ || isEmpty(LQ))
{
return false;
}
if (!recv)
{
return false;
}
*recv = LQ->front->data;
return false;
}
int getNums(LinkQueue* LQ)
{
if (!LQ)
{
return 0;
}
return LQ->length;
}
|
实际应用
线程池中的任务队列
线程池——由一个任务队列和一组处理队列的线程组成。一旦工作进程需要处理某个可能“阻塞”的 操作,不用自己操作,将其作为一个任务放到线程池的队列,接着会被某个空闲线程提取处理。
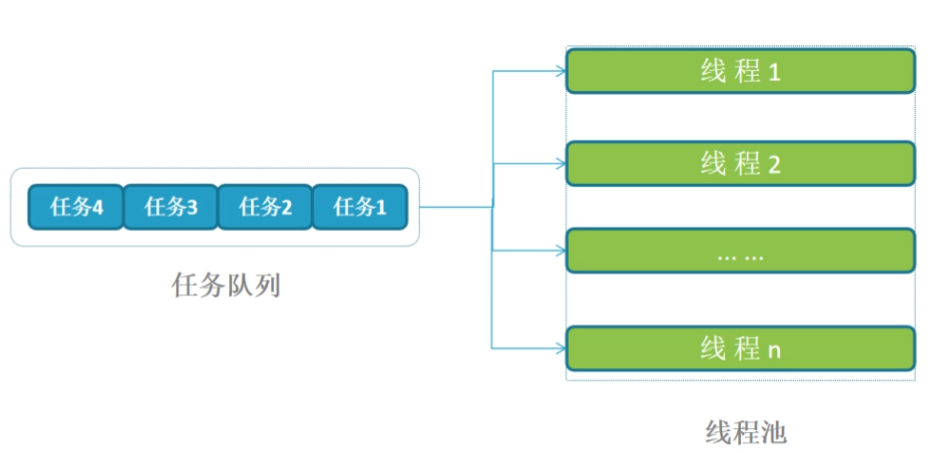
循环队列
与数组实现队列中,出队方式相关,直接移动front(假溢出),front前的元素全部抛弃,认为是空,下次直接覆盖上去。
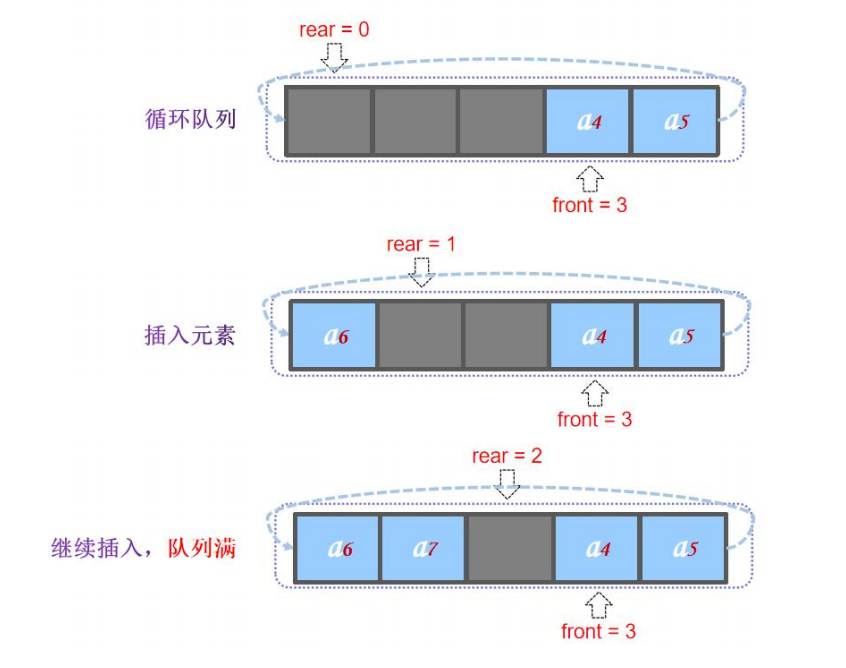
判断是否满了,rear+1是否等于front
用模运算来循环
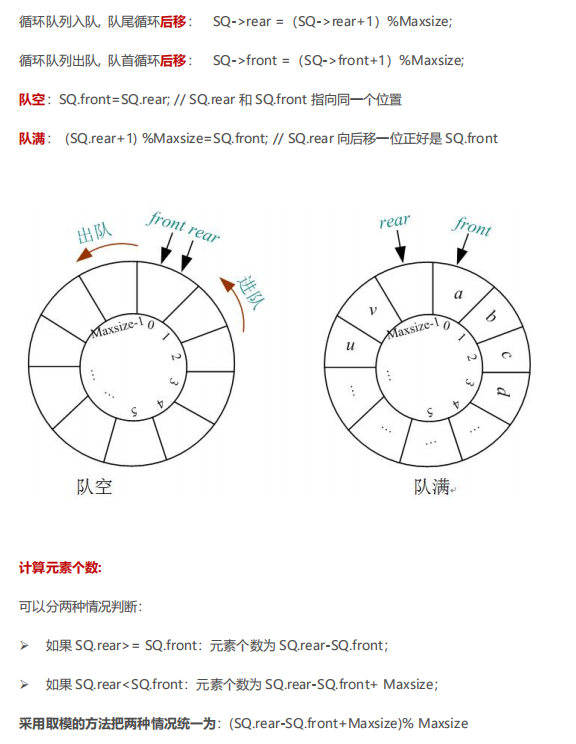
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
| typedef int DataType;
#define MAX_SIZE 10
typedef struct Queue
{
DataType queue[MAX_SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
}SeqQueue;
bool initQueue(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return false;
}
SQ->front = SQ->rear = 0;
return 0;
}
bool isFull(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return false;
}
if ((SQ->rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE == SQ->front)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool isEmpty(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return false;
}
if (SQ->front == SQ->rear)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool pushQueue(SeqQueue* SQ, DataType m_data)
{
if (!SQ || isFull(SQ))
{
return false;
}
SQ->queue[SQ->rear] = m_data;
SQ->rear = (SQ->rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
return true;
}
bool popQueue(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ || isEmpty(SQ))
{
return false;
}
SQ->front = (SQ->front + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
return true;
}
bool printQueue(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return false;
}
int index = SQ->front;
while (index != SQ->rear)
{
cout << SQ->queue[index] << " ";
index = (index + 1) % MAX_SIZE;
}
cout << endl;
return false;
}
int getElemsNum(SeqQueue* SQ)
{
if (!SQ)
{
return 0;
}
return (SQ->rear - SQ->front + MAX_SIZE) % MAX_SIZE;
}
|
优先队列
它的入队顺序没有变化,但是出队的顺序是根据优先级的高低来决定的,优先级高的先出。
还是要对比顺序存储和链式存储rear指向位置。
顺序存储rear指向最后一个的下一个位置
链式存储rear指向最后一个
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
| using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 10
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct Qnode//结点结构
{
int priority;
DataType data;
struct Qnode* next;
}Qnode;
typedef struct Queue//队列结构
{
int length;
Qnode* front;
Qnode* rear;
}Queue;
bool initQueue(Queue* Q)
{
if (!Q)
{
return false;
}
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;
Q->length = 0;
return true;
}
bool isEmpty(Queue* Q)
{
if (!Q)
{
return false;
}
if (Q->front == NULL)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool isFull(Queue* Q)
{
if (!Q)
{
return false;
}
if (isEmpty(Q))
{
return false;
}
if (Q->length == MAX_SIZE)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool pushQueue(Queue* Q, DataType _data, int _priority)
{
if (!Q)
{
return false;
}
if (isFull(Q))
{
return false;
}
Qnode* _node = new Qnode;
_node->priority = _priority;
_node->data = _data;
_node->next = NULL;
if (isEmpty(Q))
{
Q->front = Q->rear = _node;
}
else
{
Q->rear->next = _node;
Q->rear = _node;
}
Q->length++;
return true;
}
bool popQueue(Queue* Q)
{
if (!Q || isEmpty(Q))
{
return false;
}
Qnode* recvPrev = NULL;
Qnode* start = NULL;
Qnode* startNext = NULL;
Qnode* deleteTmp = NULL;
start = Q->front;
startNext = start->next;
recvPrev = start;
if (!startNext)
{
delete start;
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;
Q->length--;
return true;
}
while (startNext)
{
if (startNext->priority > start->priority)
{
recvPrev = start;
}
start = startNext;
startNext = startNext->next;
}
Qnode* difFandS = NULL;
difFandS = Q->front->next;
if (recvPrev->priority > difFandS->priority)
{
delete recvPrev;
Q->front = difFandS;
Q->length--;
return true;
}
deleteTmp = recvPrev->next;
recvPrev->next = deleteTmp->next;
delete deleteTmp;
Q->length--;
return true;
}
bool printQueue(Queue* Q)
{
if (!Q)
{
return false;
}
if (isEmpty(Q))
{
cout << "空的,别打印了" << endl;
return false;
}
Qnode* tempnode = Q->front;
while (tempnode)
{
cout << "<" << tempnode->data << "," << tempnode->priority << ">" << " ";
tempnode = tempnode->next;
}
cout << endl;
return true;
}
bool clearQueue(Queue* Q)
{
if (!Q)
{
return false;
}
Qnode* tempnode = NULL;
while (Q->front)
{
tempnode = Q->front->next;
delete Q->front;
Q->front = tempnode;
}
Q->front = Q->rear = NULL;
Q->length = 0;
return false;
}
|
动态顺序队列
使用链式存储(链表)实现的队列即为动态顺序队列,前面已经实现过,不再重复。
高并发WEB服务器队列的应用
在高并发 HTTP 反向代理服务器 Nginx 中,存在着一个跟性能息息相关的模块 ——文件缓存。
经常访问到的文件会被 Nginx 从磁盘缓存到内存,这样可以极大的提高 Nginx 的并发能力,不过因为 内存的限制,
当缓存的文件数达到一定程度的时候就会采取淘汰机制,
优先淘汰进入时间比较久或是最近访问很少(LRU)的队列文件。
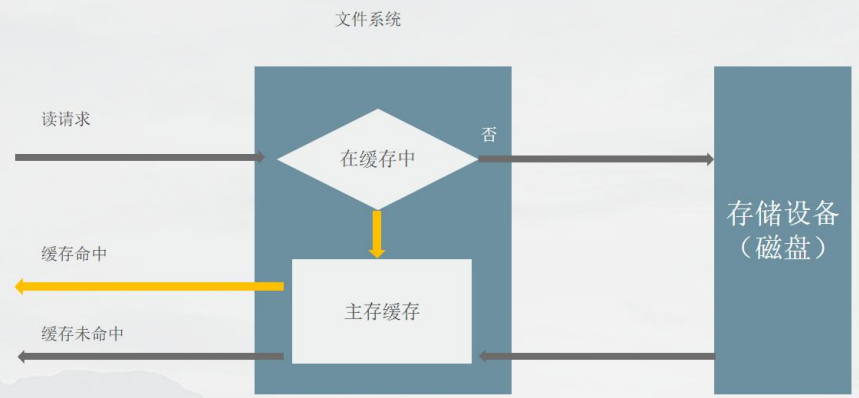
具体实现方案:
使用双向循环队列保存缓存的文件节点,这样可以实现多种淘汰策略:
比如:如果采用淘汰进入时间比较久的策略,就可以使用队列的特性,先进先出
如果要采用按照 LRU(进入时间 or 最近访问较少),就遍历链表,找到节点删除。









